There are several reasons why you should regularly check the salt level in your pool. Salt is an essential component to maintaining a clean and safe swimming environment, and as such, it’s important to ensure that the salt levels are within the recommended range.

The main advantage of checking salt level in pool is being able to ensure the safety and comfort of swimmers. Saltwater pools are known for their gentle and soothing feel, making them a popular choice among pool owners. However, maintaining the correct salt level is crucial to enjoying these benefits. In this blog post, You will learn in detail how to check salt level in pool.
Step-by-step Instructions for How to Check Salt Level in Pool
Step 1: Inspect the Pool
First and foremost, you need to inspect your pool to determine its overall condition. Make sure that there are no visible signs of excessive algae growth or debris in the water as this can affect the accuracy of your salt level test.
Step 2: Understand Salt Water Pools
It is important to understand that saltwater pools work differently than traditional chlorine pools. Instead of using granular or liquid chlorine, saltwater pools use a salt-chlorine generator to produce chlorine from the added salt. Therefore, it is essential to maintain the proper salt level in your pool for effective sanitation.
Step 3: Gather Materials
Before you start testing the salt level in your pool, make sure you have all the necessary materials on hand. These include a saltwater test kit, a clean container for collecting water samples, and the instructions for the specific test kit you are using.
Using your clean container, collect a sample of pool water from elbow depth. This will ensure that you get an accurate representation of the overall salt level in your pool.

Step 4: Test Salt Level
Follow the instructions on your test kit to perform the salt level test. Typically, this involves adding a few drops of reagent to the water sample and comparing the color change to a chart that indicates the salt level in parts per million (ppm).
Once you have completed the test, make sure to record your results for future reference. This will help you track changes in your pool’s salt level and maintain it at the appropriate range.
Step 5: Check for Optimal Salt Level
The optimal salt level for a saltwater pool is typically between 2500-4000 ppm. However, it is recommended to check with your specific pool manufacturer for the ideal range as it may vary based on the type of salt-chlorine generator you have.
If your test results show that the salt level in your pool is too low, you will need to add more salt. Use a pool calculator to determine the amount of salt required based on your pool’s size and current salt level. It is important not to add too much salt as this can cause damage to your pool equipment.

Step 6: Retest Salt Level
After adding salt, wait at least 24 hours before retesting the salt level in your pool. This allows the salt to dissolve and distribute evenly throughout the water. Repeat the testing process until you reach the optimal range.
To ensure that your pool remains properly balanced, it is essential to maintain a consistent testing schedule. Aim to test the salt level in your pool at least once a week and adjust as needed. This will help keep your pool clean and safe for swimming all season long.
Precautions for How to Check Salt Level in Pool
- When working with pool chemicals, it is important to wear protective gear such as gloves and goggles to avoid any potential skin or eye irritation.
- Pool chemicals can be harmful, so make sure to keep all testing materials out of reach of children and pets.
- Make sure to carefully read and follow the instructions provided with your test kit. This will ensure accurate results and prevent any potential accidents.
- When collecting a water sample, try not to come into direct contact with the pool water as it may contain harmful bacteria or chemicals.
- It is crucial to check the salt level in your pool before allowing anyone to swim. This will ensure that the water is safe for swimming and prevent any potential skin or eye irritation.
- When adding salt or other pool chemicals, make sure to use caution and follow all safety precautions, such as wearing gloves and avoiding contact with eyes and skin.
- When not in use, make sure to properly store all pool chemicals in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and out of reach of children and pets. This will help prevent any potential accidents or hazards.

Overall, maintaining the proper salt level in your pool is crucial for ensuring clean and safe swimming water. With these tips and precautions in mind, you can confidently and accurately test the salt level in your pool and make any necessary adjustments for optimal pool maintenance.
What Are Some Common Signs of Low or High Salt Levels in a Pool?
As a pool owner, it is important to regularly check and maintain the salt level in your pool. This ensures that your pool remains clean and safe for swimming. The most efficient way to check the salt level of your pool is by using a saltwater test kit or an electronic salt tester.
1. Saltwater Test Kit
A saltwater test kit typically consists of a sample vial, test strips or reagents, and a color chart. To use this kit, you will need to collect a water sample from your pool in the vial. Then, add the corresponding test strip or reagent into the vial and mix it with the water sample. After a few minutes, compare the color of the solution with the color chart included in the kit. The color chart indicates the salt level in parts per million (ppm) and lets you know if it’s high, low, or within the recommended range.
2. Electronic Salt Tester
An electronic salt tester is a more advanced tool that helps to quickly and accurately measure the salt level of your pool. It works by using electrodes to detect the conductivity of the water sample. To use this tester, you simply need to dip it into the water and press the start button. Within a few seconds, the salt level will be displayed on the screen.
3. Signs of Low Salt Level
Low salt levels in your pool can cause multiple problems such as algae growth and cloudy water. If you notice any of these signs, it’s essential to check your pool’s salt level:
- Green or yellow algae growth
- Cloudy or dull pool water
- Excessive foaming in the water
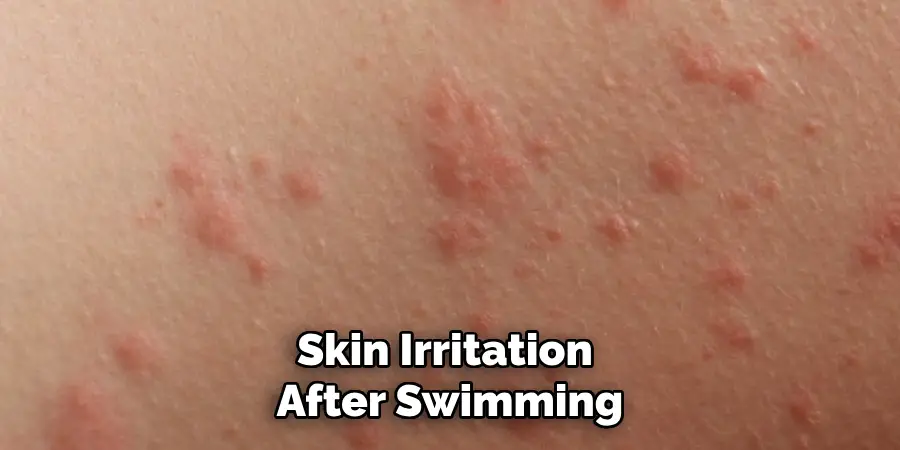
4. Signs of High Salt Level
On the other hand, high salt levels can also be harmful to your pool and swimmers. Some common signs of high salt levels include:
- Skin irritation after swimming
- Damaged pool equipment such as liners and heaters
- Metallic taste in the water
Is There Any Special Maintenance Required for Pools With a Saltwater System?
Pools with a saltwater system require some special maintenance to ensure that the salt level remains within the recommended range. Here are a few tips to keep in mind:
- Regularly test and adjust the pH level of your pool, as high or low pH can affect the effectiveness of chlorine production.
- Keep an eye on your pool’s total dissolved solids (TDS) level, as it can also impact the salt level. If your TDS levels are high, you may need to partially drain and refill your pool.
- Check the condition of your salt cell or generator and clean it regularly to prevent buildup and ensure proper functioning.
By following these maintenance tips, you can help maintain a healthy and well-balanced salt level in your pool. Remember, it’s always better to regularly check the salt level rather than waiting for signs of low or high levels. This will help prevent any potential problems and ensure your pool remains clean and safe for swimming all year round.
Are There Any Environmental Factors That May Affect the Salt Level in Your Pool?
Environmental factors can significantly affect the salt level in your pool. As a pool owner, it is essential to understand these factors and how they may impact the salt levels in your pool.
1. Rainfall
Heavy rainfall can dilute the salt concentration in your pool. This dilution can be significant, especially if you live in an area that experiences frequent heavy rain showers. In this case, it is essential to check the salt levels in your pool after a heavy downpour and add salt if necessary.
2. Evaporation
Evaporation can also affect the salt level in your pool. As water evaporates from your pool, the salt concentration increases, potentially leading to higher than normal salt levels. It is crucial to regularly top up your pool with fresh water to maintain the proper salt balance.
3. Humidity
High humidity can also impact the pool’s salt levels. When humidity is high, less water evaporates from your pool, leading to lower salt concentrations. Conversely, low humidity can cause more evaporation and result in higher salt levels.
4. Temperature
The temperature of your pool’s water can also affect the salt levels. Higher temperatures can cause more rapid evaporation, leading to increased salt levels. On the other hand, cooler temperatures may cause lower salt concentrations due to less evaporation.
5. Pool Usage
The usage of your pool can also impact the salt levels. Swimmers bring in organic materials such as sunscreen and sweat that can break down into chlorine demand, reducing the effectiveness of salt chlorine generators. This can lead to lower salt levels in your pool, requiring you to add more salt to maintain the proper balance.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the salt level in your swimming pool is a crucial factor to maintain for a safe and enjoyable swimming experience. As discussed, there are various methods to check the salt level in your pool, including using test strips, electronic meters, or hiring a professional service. It is important to regularly monitor and adjust the salt level if needed, as too high or too low levels can result in various issues, including skin and eye irritation, damage to pool equipment, and algae growth.
By following the recommended procedures and taking necessary measures, you can ensure that your pool’s salt level is at an optimal level for a clean and inviting swimming experience. I hope this article has been beneficial for learning how to check salt level in pool. Make Sure the precautionary measures are followed chronologically.
About
Outdoor Fixes is a distinguished figure in the world of Diy design, with a decade of expertise creating innovative and sustainable Diy solutions.
His professional focus lies in merging traditional craftsmanship with modern manufacturing techniques,
fostering designs that are both practical and environmentally conscious. As the author of diy,
outdoorfixes delves into the art and science of outdoorfixes-making, inspiring artisans and industry professionals alike.
Education RMIT University
(Melbourne, Australia) Associate Degree in Design (Outdoor Fixes) Focus on sustainable design, industry-driven projects,
and practical craftsmanship. Gained hands-on experience with traditional and digital manufacturing tools, such as CAD and CNC software.
Nottingham Trent University
(United Kingdom) Bachelor’s in outdoorfixes.com and Product Design (Honors) Specialized in product design with a focus on blending creativity with production
techniques. Participated in industry projects, working with companies like John Lewis and Vitsoe to gain real-world insights.
Publications and Impact
In diy, Outdoor Fixes his insights on indoor design processes, materials, and strategies for efficient production.
His writing bridges the gap between artisan knowledge and modern industry needs, making it a must-read for both budding designers and seasoned professionals.

